
Pd runs under Irix, Microsoft Windows, Linux, and MacOS 10.2 (Jaguar). How to get Pd up and running depends on your operating system, but the overall strategy is the same. You must first get and install it, and then untangle whatever problems arise in handling audio and MIDI input and output, and finally get Pd to meet its real-time obligations reliably.
Installation instructions are platform-specfic; the following four sections will describe what to do for various operating systems you might have. In case of trouble also consult the Pd mailing list archive on http://iem.kug.ac.at/mailinglists/pd-list/ , which often has late-breaking news about configuration problems and solutions. The rest of this section describes how to get audio and MIDI to work.
To test audio and MIDI, start Pd and select "test Audio and MIDI" from the "Media" menu. You should see a window like this:

First, try to get Pd to play a sine wave over your speakers. The "TEST TONE" control at top left turns this on and off. Normally, all the output channels are turned on so that when you turn the tone on (to a soft -40 dB or a louder -20 dB) you should get output on the first six of your output channels. (If you have fewer than six output channnels open, the extra channels aren't played; and if you have more, this particular patch won't use them.)
If there's anything wrong, the most likely outcome is that you will hear nothing at all. This could be for any of at least three reasons: Pd might have failed to open the audio device; the audio card's output volume might be set to zero; or your audio system might not be set to amplify the computer output.
The number boxes labeled "AUDIO INPUT" show the levels of incoming audio, in dB, with 100 being maximum. (Incoming signals may clip at RMS levels below 100; for instance, a sinusoid clips at about 97 dB.) Any DC present in the input (such as you get with cheap audio hardware) will show up as level unless you turn on the "input hipass" toggle at right; then the DC component is filtered out before metering.
To test the quality of audio input and output, turn on "monitor" (also at right) which causes the inputs to be played to the outputs at unit gain. You should hear a faithful, non-distored copy of whatever is sent through the patch.
It is easy to get two copies of Pd running by accident; on most machines only one at a time may be inputting and outputting sound. (Some copy of Pd might have audio or MIDI devices open and prevent the copy you're trying to use from getting access to them.) Having extra copies of Pd around will also eat CPU cycles uselessly.
You may be interested in getting only audio output or audio input, or you may need both to run simultaneously. By default, Pd will try to run both, but if you don't need either input or output, you may find that Pd runs more reliably, or at least more efficiently, with the unused direction turned off. This may be specified in Pd's command line flags or using the "audio settings" dialog panel.
Depending on your application you will have a more or less stringent latency requirement. Ideally, when any input (audio, MIDI, keyboard, network) is available, the outputs (in particular the audio output) should react instantly. In real life, it is necessary to buffer the audio inputs and outputs, trying always to keep some number of milliseconds ahead of real time to prepare for the inevitable occasions where the CPU runs off to service some different task from Pd. How small this latency can be chosen depends on your OS and your audio driver.
TIP: If Pd starts up but you get distortion or glitches in the audio output, this could be either because the "audio I/O buffer" isn't big enough, or else because the CPU load of the patch you're running is too great for the machine you have, or else because the ADC and DAC are out of sync or even at different sample rates. To test for the first possibility, try increasing the audio latency in the command line or the "audio settings" dialog (but see also under your OS below.) For the second, start up your favorite performance monitor program; and for the third, try starting Pd up with ADCs disabled.
In addition to the "test audio and MIDI" patch, the "Media" menu contains items for controlling audio and MIDI settings. The first two items, "Audio on" and "Audio off", open or close the audio devices and start or stop Pd's audio computation.
If there is a choice of audio API to make, the Media menu will display them. (On Linux, they are OSS, ALSA, and Portaudio; on Windows, you get MMIO and ASIO). More information about the APIs appears in the sections below.
Next is the "Audio settings..." menu item, which opens a dialog like this:
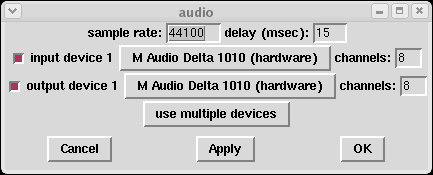
Next you get a choice of input and output device. If you want to open more than one, hit "use multiple devices" and you'll be allowed up to 4 in and 4 out. Each audio device is 2 channels by default, but you may specify more if your hardware supports it.
Pd is compiled under NT, but should work under any version of Windows since 95. Pd will appear as a self-extracting archive (a ".exe" file). Run this and select a destination directory when prompted, such as "\pd" or "Program Files\pd".
If for example you put Pd in "C:Program Files\pd", the executable program will be "C:Program Files\pd\bin\pd". You can simply adjust your path to include C:\pd\bin and then invoke "pd" in a command prompt window. You can also make a shortcut to the executable program (left-click on it and drag to the desktop, for example.)
Pd requires "TCP/IP networking" to be turned on. This doesn't mean you have to be on a real network, but simply that Pd actually consists of two programs that make a "network link" (locally) to intercommunicate.
Pd is a "command line" program. Most error and diagnostic messages from Pd appear on the command prompt window Pd runs from.
If you start Pd from the "run" menu or as a shortcut, and if there's a problem with run-time flags (see the Pd command line below), Pd will print an error and exit. You won't see this error unless you arrange for the "command prompt" or "msdos" window to stay open after Pd exits. One way to do this is to make a "batch" file ("run.bat", say) containing the Pd command line.
You can ask for a list of audio and MIDI devices by typing "pd -listdev"; you can then specify which audio and MIDI device to use. Type "pd -help" (or make any mistake) to get the syntax for specifying which device to use. You can modify the Pd shortcut (or batch file) to set these.
Alternatively, (and especially when just starting out) you can experiment with different audio configurations using the "audio settings" item in the Media menu.
You can list and choose MIDI devices in the same way as audio; note that, by default, MIDI input is disabled in Windows (because it's possible to hang up some MIDI devices if Pd exits unexpectedly).
MIDI timing is very poor if you are using simultaneous audio input and output; if you suppress either audio input or output things will improve somewhat under NT; you can apparently get the jitter down to ~40 msec. On W95 performance is simply terrible. W98, with either audio input or output suppressed, offers fairly good MIDI timing (~5 msec jitter). The "first edition" used to crash occasionally; this might be fixed in the "second edition".
Some NT and W98 drivers greet you with a constant trail of "resyncing audio" messages. Sometimes you can fix this by invoking Pd with the "-noresync" flag.
As of version 0.35 Pd supports ASIO. Invoke Pd as "pd -asio" and, if needed, specify "-sounddev" (etc.) flags to specify which device (see "the Pd command line" below.) You can also specify a "-blocksize" different from the default (256 samples) and "-audiobuf" in milliseconds. Pd will round this down to a power of two buffers, each of "-blocksize" in sample frames.
What to do depends on which flavor of Linux you are running (e.g., Debian or Red Hat). The instructions here should work for Pd 0.33 and up regardless of your situation. (If not, you can read the Pd mailing list archives for recent problems; if you have found a new problem you're welcome to post it to the list.)
If you're running RedHat or Mandrake you might want to use RPM to install Pd. For other linux distributions, download the "tar.gz" version and compile Pd.
Download Pd, perhaps from http://www.crca.ucsd.edu/~msp/software.html , to a file such as "pd-0.33-0.i386.rpm". Open a "shell" window, cd to the directory containing the file, and type the command,
rpm -i pd-0.33-0.i386.rpm
(substituting the real file name.) Then you should be able to type "pd" to a shell and watch the Pd main window appear.
Before you start, you might want to check that you have the resources Pd needs. The main things you need are the C compiler, X windows (including the X development package for Pd to link against) and TK. If you're running Redhat or Mandrake 7.x or up, I think these are all present by default. The RedHat X client developer "RPM" package is called XFree86-devel.
Download Pd, perhaps from http://www.crca.ucsd.edu/~msp/software.html , to file such as "pd-linux-033.tar.gz". Open a "shell" window, cd to the directory containing the file, and type the command,
tar xzf pd-linux-033.tar.gz
which creates a directory named "pd". I do this from my home directory. Next, compile it. "CD" to pd and read the INSTALL.txt, or else just cd to "pd/src" and type
./configure
make depend
make
You can pass flags to "configure" to customize your compilation:
To enable debugging (and losing code optimization) add "--enable-debug".
To use Portaudio version 19 (experimental), add "--enable-portaudio".
To put Pd in /usr/bin instead of /usr/local/bin, add "--prefix=/bin".
Alsa and Jack support should auto-configure, but "--enable-alsa" od
"--enable-jack" will force their inclusion.
After "make", just type "~/pd/bin/pd" to run pd.
Alternatively, as superuser, you can run "make install" after "make depend" and then anyone on your system can just type "pd" to run it.
Next try audio. We want to know whether audio output works, whether audio input works, and whether they work simultaneously. First run "aumix" (or any newer audio mixer app) to check audio input and output gains and learn which input (mic; line; etc.) is "recording". Then test audio output by running
pd -noadc
and selecting "test audio and MIDI" from the "Media" menu. You should see a patch. Turn on the test tone and listen. Do the usual where's-the-signal business.
Then quit Pd and test audio input via
pd -nodac
Re-open the test patch and hit "meter"; look at the levels. 100 dB is a hard clip; arrange gains so that the input signal tops out around 80 or 90, but no higher.
Now see if your audio driver can do full duplex by typing "pd" with no flags. If you see error messages involving /dev/dsp or /dev/dsp2, you're probably not able to run audio in and out at the same time. If on the other hand there's no complaint, and if the audio test patch does what you want, you might wish to experiment with the "-audiobuffer" flag to see what values of audio latency your audio system can handle.
Be forewarned: installing and testing audio and MIDI drivers in Linux can take days or weeks. There apears to be no single place where you can get detailed information on Linux audio.
Depending on your hardware and software, you might or might not be able to run "full duplex," i.e., use audio input and output at the same time. For many applications it's important to be able to do this, but if by any chance you don't need simultaneous input and output you will have much less trouble than if you do.
There are two widely-used driver sets, called "OSS" and "ALSA". OSS is included in the standard Linux kernels since version 2.2. However, for some audio cards you can find newer versions than are included in the kernel releases. You can get ALSA from http://www.alsa-project.org/ .
ALSA is able to emulate OSS, so that you can usually run Pd using the default "OSS" settings even if it's actually ALSA that's running.
OSS is really a collection of loadable device drivers. The commands for loading and unloading the drivers are "insmod" and "rmmod". You can see if the audio drivers are running using "lsmod" (as root.) If you see something like:
Module Pages Used by eepro100 3 1 (autoclean) opl3 3 0 opl3sa2 1 0 ad1848 4 [opl3sa2] 0 mpu401 5 [opl3sa2] 0 sound 15 [opl3 opl3sa2 ad1848 mpu401] 0 soundcore 1 [sound] 6 soundlow 1 [sound] 0 aic7xxx 23 2
then OSS is running, and if all you see is:
eepro100 3 1 (autoclean) aic7xxx 23 2
then it isn't. You can turn OSS off by running "rmmod" repeatedly, starting with "opl3" (or whatever) so as not to remove any module before you remove all the modules that depend on it. In the above listing, "opl3*" is device dependent and you might see different names.
The file, "/etc/modules.conf" apparently controls which sound drivers are started at boot time. The sndconfig program updates this file but you can also change things manually, for instance to switch between two different sound cards. In Redhat 6.x and earlier, the file is named "conf.modules."
Here is a modules.conf file for OSS:
alias eth0 e100 alias parport_lowlevel parport_pc alias char-major-81 bttv alias usb-controller usb-uhci alias sound-slot-0 i810_audio alias sound-slot-1 es1371
Here the two sound cards are the (motherboard resident) i810 driver and an ensoniq es1371.
In RedHat at least, the "sndconfig" program tries to automatically search for your soundcard. Unfortunlately it only finds the "first" one which is often not the one you want to use!
Under OSS, programs can stream sound using either "block" or "stream" mode. Stream mode is the more modern and better of the two, but the majority of drivers, even for new sound cards, only support "block." Pd makes "block" the default.
ALSA is newer, hence less stable and harder to use, than OSS. Alsa comes in a "finished" version (0.5.x) and a different, redesigned, "beta" version, 0.9. Installing ALSA can be tricky and/or confusing.
As of version 0.37 Pd works only with 0.9.x versions. The RPM version of Pd is compiled for 0.9.x.
By default, Pd uses OSS. If you are running ALSA, Pd will use ALSA's OSS emulation. To make Pd use ALSA "natively", i.e., the way ALSA is designed to be used, include the "-alsa" flag in the command line.
In ALSA, you can specify which sound card to use using the "-alsadev" flag. So, for instance, "-alsadev 3" means your third card, counting from one. You can also specify it the ALSA way: "-alsadev hw:3,0".
Here's a rundown on my experiences with sound cards so far. See also the Pd mailing list archives.
This is the best sound card out there; it costs around $500 and has 3 ADAT I/O ports and one SPDIF. There is a "baby hammerfall" also, which I think is the "9632." DO NOT CONFUSE THE 9652/9632 WITH OTHER RME BOARDS WHICH MIGHT NOT WORK WITH PD.
Word on the Pd mailing list is that the only way at present (7/04) to use Hammerfall boards in Pd is via ALSA and jack.
Midiman sells PCI devices (delta 44, 66, 1010, and 1010LT) with between 4 and 10 channels in and out, for which there are ALSA drivers. The driver name is "ice1712".
Alsa provides an "envy24control" program (in "utils". You should run this and check that your ice1712's sync source is internal if you have no SPDIF input, or "SPDIF" if you do. I think the default is now "internal" but don't take it for granted...
In RedHat 7.0, motherboards with native i810 audio systems don't work in full duplex (they crash linux). Either run Pd -noadc or else (better) install ALSA.
Pd version 0.35 and up support Macintosh OSX. You need the OSX Jaguar distribution (10.2) or later.
To install Pd you can always just download the sources and compile them yourself, or (easier) find a MacOSX-style "package". The first package was put together by Adam Lindsay; the most current one seems to be the one by Hans on http://www.pure-data.info/Members/hans/. The package simply installs itself and you needn't follow the directions below.
The binary tarballs on http://www.crca.ucsd.edu/~msp/software.html take more steps to install but are more "official". To install them:
If you haven't already, first download and install Tcl/Tk; there are pointers on Hans's page, or try: http://tcltkaqua.sourceforge.net/ http://tcltkaqua.sourceforge.net/. Double click on what you get (a disk image opens) and then double click on the "package" icon, and the installer should tell you how to proceed from there.
Then download a tarball like pd-0.37-0.mac.tar.gz, and expand it (I think that's done just by clicking on the thing in OSX.) You can install it into your home directory for example. Then start a shell window and type "~/pd/bin/pd" to it, and pd should start.
Whether you've downloaded the source or the "package" you can always compile Pd for yourself, whether to make your own improvements, or possibly so that you can get the newest version before it shows up compiled for Mac OS X.
To be able to compile Pd, you must have installed Tcl/Tk specifically in /Applications/Wish Shell.app and /Library/Frameworks/Tk.framework and /Library/Frameworks/Tcl.framework.
First download and install TK for OSX as described above.
Then, just as for linux, just unload pd-whatever.tar.gz into a directory such as ~/pd-0.36-0, cd to pd-0.36-0/src, type "./configure" and "make". Then type ~/pd-0.36-0/bin/pd to a shell and enjoy!
If you wish you can put a line such as,
alias pd ~/pd/bin/pd
in the file, ~/.tcshrc, so that you can later just type "pd" to a shell. (The shell only reads the ~/.tcshrc file on startup, so this won't take effect in any existing shells unless you specially type
source ~/.tcshrc
to them.)
In some cases you have to explicitly give "-soundindev" and "-soundoutdev" flags for Pd to open audio correctly; "pd -listdev" should show you the correct device numbers.
To get MIDI working, you have to do the Mac OSX magic to get a USB MIDI interface installed. I've seen this done with Midisport devices and I think you just download the OSX driver and follow directions.
On the machine I tried, it was necessary to type,
pd -midiindev 1 -midioutdev 2
to get MIDI working.
(NOTE: as of release 0.35 I haven't had an IRIX machine to compile Pd on. Soeren Bovbjerg has kindly compiled 0.35 and 0.36 for IRIX; you can find these at http://www.cvmt.dk/~sb/ .)
Download Pd, which will be a "tar.Z" file. You can unpack this by typing "zcat [name].tar.Z | tar xf -" to a shell. This creates a directory named "pd".
Starting with release 0.25, Pd should come in "n32" and "o32" versions. "o32" is the default and will run on IRIX 5.x and up. "n32" runs faster, but only on 6.x and up. Also, "externs" have to be updated for n32. The "pd" executable (bin/pd in the distribution) is a symbolic link to either "pd-o32" or "pd-n32."
NOTE: "externs" appear to be broken in the N32 version... I'm not sure how long this has been true. If you want to use external objects, you have to use the O32 version.
If for example you put Pd in ~, the executable program will be ~/pd/bin/pd. The program looks at its command line to figure out where it is, so it's best to invoke Pd by its full pathname. You should always invoke Pd from a Unix shell because many important messages appear on the standard error.
The simplest way to invoke Pd is to make an alias in your ".cshrc" file (assuming you use the "c" shell) such as:
alias pd ~/pd/bin/pd
(assuming your Pd distribution landed in ~, for example).
Pd will open the "default" audio input and output devices, without regard for whether they are in sync or not. This will be bad if they aren't; use the "-noadc" or "-nodac" flag to disable either the input or output. Pd is supposed to handle up to 8 channels of audio in and/or out. (But at least one user had to recompile Pd on his Onyx to get 8 channels working.)
As to MIDI, Pd simply attempts to open all available MIDI devices for input and output, which is probably very bad on anything more recent than my Indy. If any MIDI ports fail to open either for input or output, all MIDI is disabled.
Pd has not been fixed to request real-time priority from Irix; it will compete with all other processes on your machine for CPU time.
Pd takes command line arguments to set the number of input and output channels and the sample rate. These don't affect the SGI's audio settings, which you have to set separately using the "audio panel." Pd does detect the audio sample rate if you don't specify one on the command line.
On SGI machines, you have to work to get MIDI running. Before you start Pd, verify that least one MIDI port is configured open. Pd opens the FIRST MIDI port that's open. You might want to get rid of the "software" MIDI port if you're running 6.x. On Indys, the usual practice is to open serial port number 2 because some systems configure port 1 as "console" by default. You can use the GUI if you want, or else just type
startmidi -d /dev/ttyd2
to get port 2 speaking MIDI, and
stopmidi
to stop it. You can test whether MIDI is configured by typing,
ps -dafe | grep midi
and looking for "startmidi" processes.
It's a good idea to connect your serial port to your MIDI interface before typing the "startmidi" command, not afterward, at least in 5.x. We use the Opcode Studio 3 interface but in principle any Mac-compatible one should work.
The O2 apparently has RS232 ports, not RS422. I think SGI's web site says something about how to deal with this.
GEM, originally by Mark Danks but now supported by Iohannes Zmoelnig, is essentially an extension of Pd that allows you to do OpenGL programming using a suite of "GEM objects" roughly parallel to the tilde objects built into Pd for audio. Find out more from Johannes's page.
Pd is a "command line" program. The best way to run it is from your "terminal emulator," "shell," or "MSDOS prompt." The command line is:
pd [options] [patches to open]
although you may have to specify a path (such as "~/pd/bin/pd" or "C:\program files\pd\bin\pd") so your command interpreter can find Pd. Possible options include:
audio configuration flags:
-r <n> -- specify sample rate
-audioindev ... -- sound in device list; e.g., "2,1" for second and first
-audiooutdev ... -- sound out device list, same as above
-audiodev ... -- specify both -audioindev and -audiooutdev together
-inchannels ... -- number of audio in channels (by device, like "2" or "16,8")
-outchannels ... -- number of audio out channels (by device)
-channels ... -- specify both input and output channels
-audiobuf <n> -- specify size of audio I/O buffer in msec
-blocksize <n> -- specify audio I/O block size in sample frames
-sleepgrain <n> -- specify number of milliseconds to sleep when idle
-nodac -- suppress audio output
-noadc -- suppress audio input
-noaudio -- suppress audio input and output (-nosound is synonym)
-listdev -- list audio and MIDI devices
(linux specific audio:)
-frags <n> -- specify number of audio fragments (defeats audiobuf)
-fragsize <n> -- specify log of fragment size ('blocksize' is better...)
-oss -- use ALSA audio drivers
-alsa -- use ALSA audio drivers
-pa -- use portaudio (experimental version 19)
-alsadev <n> ----- obsolete: use -audiodev
-32bit ---- (probably obsolete) -- use 32 bit OSS extension
(Windows specific audio:)
-mmio -- use MMIO drivers and API
-asio -- use ASIO drivers and API
MIDI configuration flags:
-midiindev ... -- midi in device list; e.g., "1,3" for first and third
-midioutdev ... -- midi out device list, same format
-mididev ... -- specify -midioutdev and -midiindev together
-nomidiin -- suppress MIDI input
-nomidiout -- suppress MIDI output
-nomidi -- suppress MIDI input and output
general flags:
-path <path> -- add to file search path
-helppath <path> -- add to help search path
-open <file> -- open file(s) on startup
-lib <file> -- load object library(s)
-font <n> -- specify default font size in points
-verbose -- extra printout on startup and when searching for files
-version -- don't run Pd; just print out which version it is
-d <n> -- specify debug level
-noloadbang -- suppress all loadbangs
-nogui -- suppress starting the GUI
-guicmd "cmd..." -- substitute another GUI program (e.g., rsh)
-send "msg..." -- send a message at startup (after patches are loaded)
-rt or -realtime -- use real-time priority (needs root privilege)
Here are some details on some of the audio, MIDI, and scheduler options (but see also the next section on file management.)
You can specify multiple MIDI input and output devices. For example, "pd -midiindev 3 -midioutdev 4,2" asks for the third MIDI input device and the fourth and second MIDI output device.
Audio device selection is similar, except that you can also specify channels by device: "-audioindev 1,3 -inchannels 2,8" will try to open device 1 (2 channels) and device 3 (8 channels.)
The sample rate controls Pd's logical sample rate which need not be that of the audio input and output devices. If Pd's sample rate is wrong, time will flow at the wrong rate and synthetic sounds will be transposed. If the output and input devices are running at different rates, Pd will constantly drop frames to re-sync them, which will sound bad. You can disable input or output if this is a problem.
You can specify an audio buffer size in milliseconds, typically between 10 and 300, depending on how responsive your OS and drivers are. If this is set too low there will be audio I/O errors ("data late"). The higher the value is, on the other hand, the more throughput delay you will hear from the audio and/or control inputs (MIDI, GUI) and the audio coming out.
You can also specify the audio block size in sample frames. This is 64 by default (except for MMIO for which it's 256), and may be 64, 128, or 256.
The "sleepgrain" controls how long (in milliseconds) Pd sleeps between periods of computation. This is normally the audio buffer divided by 4, but no less than 0.1 and no more than 5. On most OSes, ingoing and outgoing MIDI is quantized to this value, so if you care about MIDI timing, reduce this to 1.
System exclusive MIDI message inupt and output is theoretically supported in version 0.37 but has not been tested.
In Linux, if you ask for "pd -midioutdev 1" for instance, you get /dev/midi0 or /dev/midi00 (or even /dev/midi). "-midioutdev 45" would be /dev/midi44. In NT, device number 0 is the "MIDI mapper", which is the default MIDI device you selected from the control panel; counting from one, the device numbers are card numbers as listed by "pd -listdev."
Pd has a search path feature; you specify the path on the command line using the "-path" option. Paths may contain any number of files. If you specify several files in a single "-path" option they're separated by colons in unix or semicolons in NT.
You can see and edit the path while Pd is running using the "path..." item in the "File" menu. The path must be correctly set before you load a patch or it may fail to find abstractions, etc., that are needed to construct the patch.
When Pd searches for an abstraction or an "extern" it uses the path to try to find the necessary file. The "read" messages to qlists and arrays (aka tables) work the same way. NO SPACES MAY APPEAR ANYWHERE IN THE SEARCH PATH, e.g., "c:\my nonsense\goobers" won't work.
Path entries may be relative to the patch directory; for instance, if your path has an item, "../sound", and your patch is in "my stuff/all mine", then Pd will look in "my stuff/sound". Spaces should be OK in the path to the patch, but not in the path entry (../sound) itself. This is useful if you have a patch and supporting files (even a supporting snapshot of pd) that you want to distribute or carry around together.
Regardless of path, Pd should look first in the directory containing the patch before searching down the path. (However, sometimes, for reasons I can't explain yet, you have to put the entry "." in the search path for this to happen, as least within linux!)
Filenames in Pd are always separated by (unix-style) forward slashes, even
if you're on Windows (which uses backslashes). This is so that patches can be
ported more easily between operating systems. On the other hand, if you
specify a filename on the command line (as in "pd -path c:\pdlib") the file
separator should agree with the operating system.
If a filename specified in a patch has any "/" characters in it, the "path" is not used; thus, "../sounds/sample1.wav" causes Pd only to look relative to the directory containing the patch. (You may also invoke externs that way.)
As of version 0.35, there may be spaces in the path to Pd itself; also, the "openpanel" and "savepanel" objects can handle spaces. But still not the search path.